Medical Device
Biomimetic materials for the next generation of implants—designed to mimic real tissue mechanics with tunable, durable LCE performance.
Biomimetic Materials for the Next Generation of Implants
Our LCE-based materials are transforming soft-tissue applications—from tendon and ligament reinforcement to joint resurfacing and replacement. Engineered for durability and performance, these biomimetic implants offer exceptional energy-dissipative properties, strong wear resistance, and a low coefficient of friction.
What We’re Building
Tunable Tissue-Like Mechanics
Anisotropic and rate-dependent behaviors allow precise tuning to mimic natural tissue function across joint and soft-tissue use cases.
Durability Under Load
Designed for demanding motion cycles—energy dissipation and low friction support long-term performance and comfort.
Regulatory Progress
Key milestones to support clinical translation, including FDA readiness activities and program advancement.
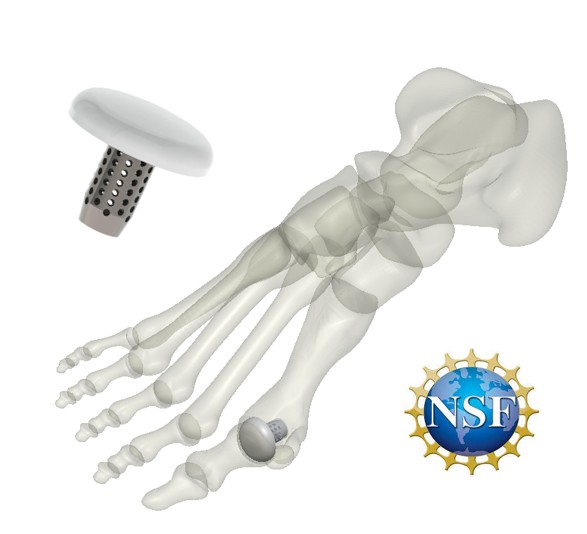
Medical Device Program
Funded by the NSF, Impressio is developing a next-generation MTP implant to treat Hallux Rigidus. Restoring natural joint movement requires materials that truly behave like real tissue—and our proprietary LCEs are uniquely capable of mimicking joint mechanics. These materials can be tailored to match performance needs across different joints throughout the body.
Impressio has officially submitted its Material Master File (MAF) to the FDA—marking a key milestone in regulatory readiness and reinforcing our commitment to safety, innovation, and clinical translation.
In April 2025, Impressio reached a key milestone with the 510(k) submission to the FDA for our next-generation MTP implant to treat Hallux Rigidus—bringing us closer to advancing joint restoration.
